Computer vision (CV) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that has been rapidly developing in recent years, thanks to the rise of deep learning. CV techniques have been applied to various manufacturing industries since the early 1970s, including food, pharmaceutical, automotive, aerospace, railway, semiconductor, electronic component, plastic, rubber, paper, and forestry-related fields. In this article, we will explore the various of computer vision applications in manufacturing industry, highlighting its potential to improve efficiency, accuracy, and safety.
Computer Vision Applications in Manufacturing
Automated Visual Inspection
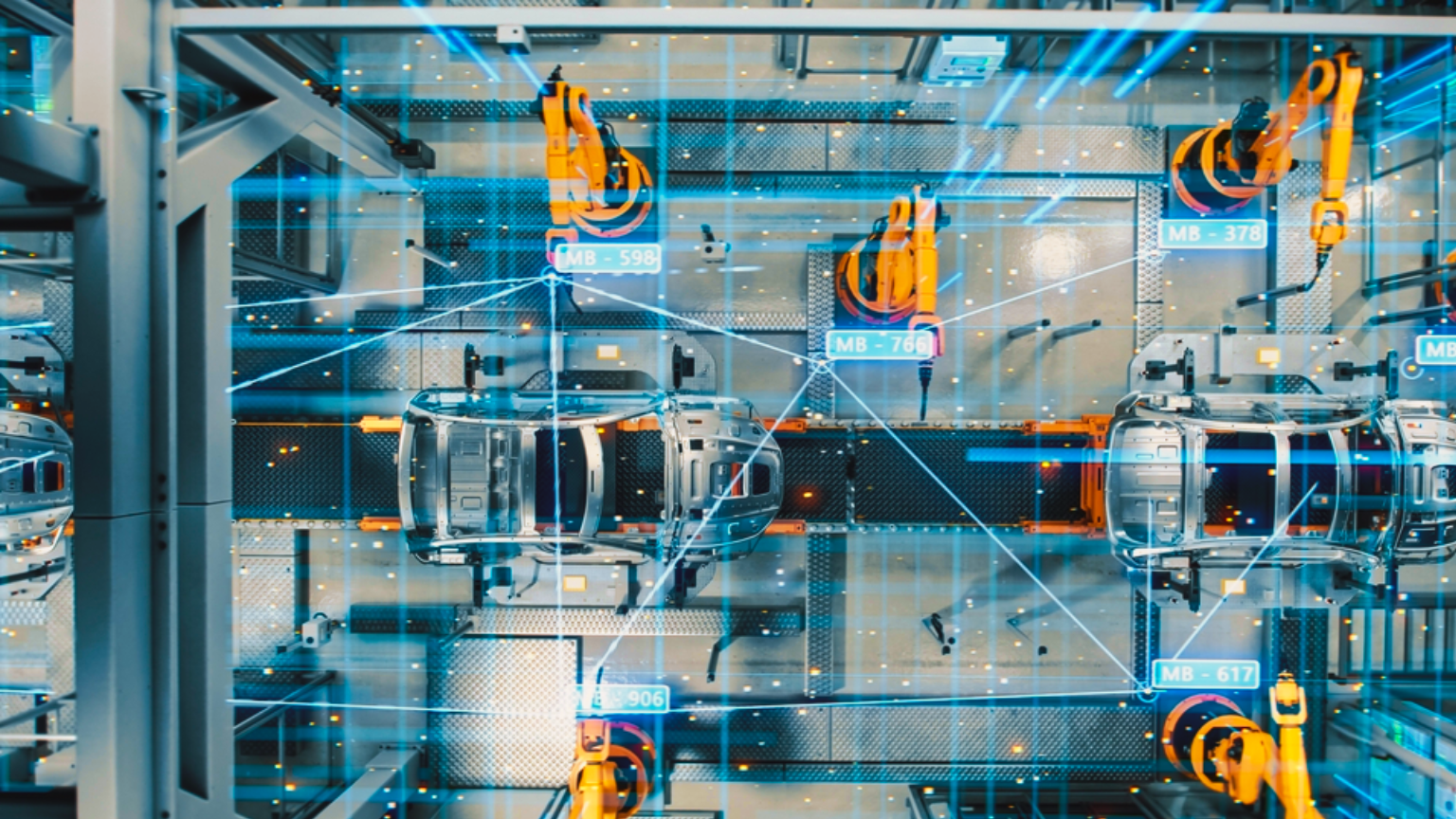
One of the most significant applications of computer vision in manufacturing is vision-based industrial inspection. This technique involves using cameras and image processing algorithms to detect defects in products during the manufacturing process. Vision-based inspection systems can detect defects that are difficult or impossible to detect with the naked eye, such as cracks, scratches, and other surface imperfections. This technology can help manufacturers identify and correct defects early in the production process, reducing waste and improving product quality.
For example, in the automotive industry, computer vision is used to inspect car bodies for defects during the manufacturing process. Cameras are placed at various points along the assembly line, and images of the car body are analyzed in real-time to detect any defects. This technology can help manufacturers identify and correct defects early in the production process, reducing waste and improving product quality.
Artificial Intelligence In Computer Vision
Quality Control and Assurance
Computer vision can also be used for quality control in manufacturing. By analyzing images of products, computer vision algorithms can detect defects and deviations from the desired specifications. This technology can help manufacturers ensure that their products meet the required quality standards, reducing the risk of product recalls and improving customer satisfaction.
For example, in the food industry, computer vision is used to inspect food products for defects, such as foreign objects or discoloration. Cameras are placed at various points along the production line, and images of the food products are analyzed in real-time to detect any defects. This technology can help manufacturers ensure that their products are safe and of high quality.
Process Monitoring and Optimization
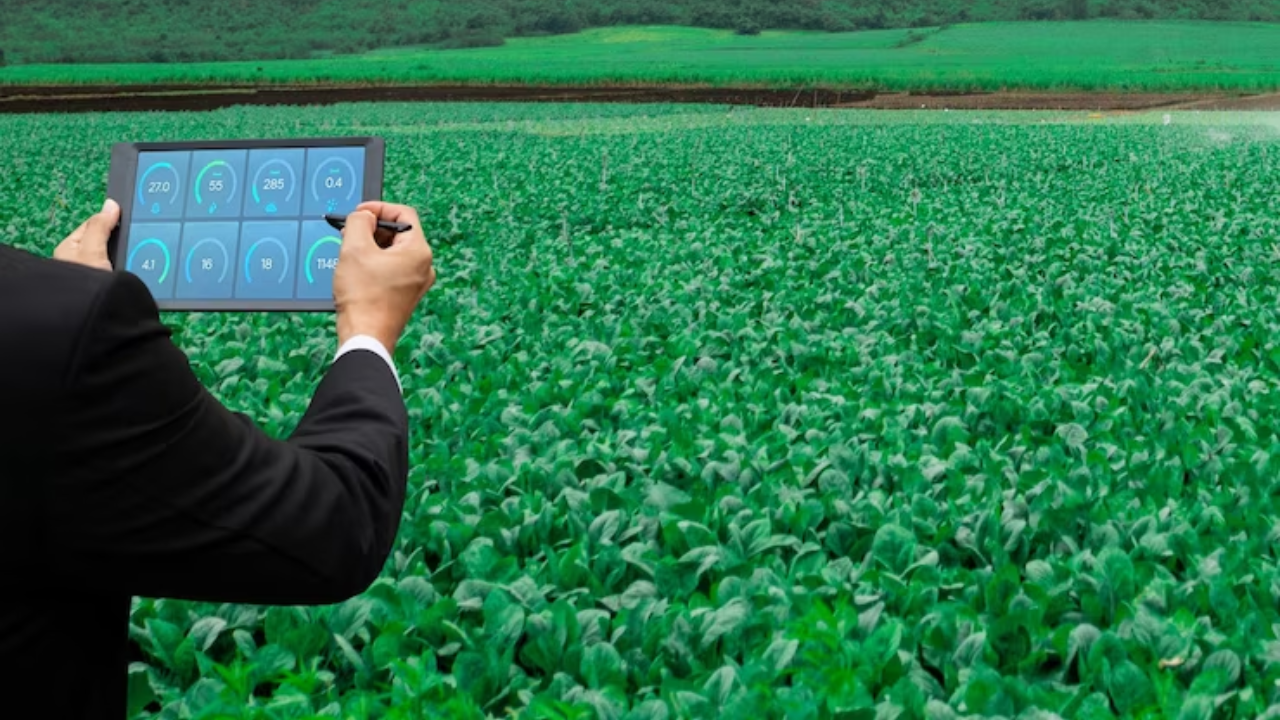
Computer vision can also be used for process monitoring and optimization in manufacturing. By analyzing images of manufacturing processes, computer vision algorithms can detect anomalies and deviations from the expected process. This technology can help manufacturers identify and correct issues in real-time, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
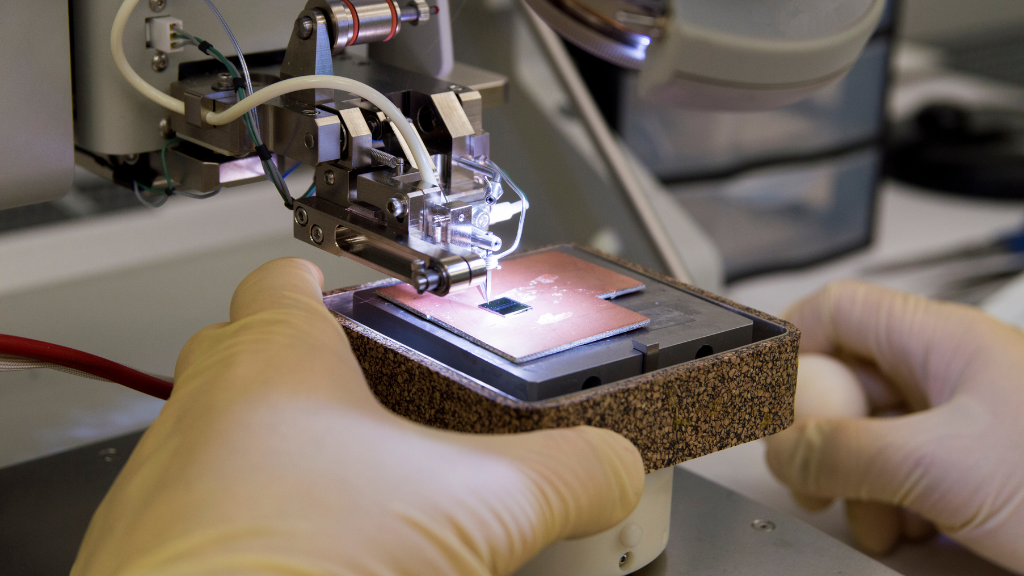

For example, in the semiconductor industry, computer vision is used to monitor the manufacturing process of computer chips. Cameras are placed at various points along the production line, and images of the chips are analyzed in real-time to detect any defects or anomalies. This technology can help manufacturers optimize the manufacturing process and improve the yield of high-quality chips.
Robotic Automation
Computer vision can also be used to improve robotic automation in manufacturing. By using cameras and image processing algorithms, robots can detect and manipulate objects with greater accuracy and precision. This technology can help manufacturers automate repetitive and dangerous tasks, reducing the risk of workplace injuries and improving efficiency.
For example, in the electronics industry, computer vision is used to guide robots in the assembly of electronic components. Cameras are placed above the assembly line, and images of the components are analyzed in real-time to guide the robots in the assembly process. This technology can help manufacturers automate the assembly process and improve the accuracy and speed of production.
Vector Search in Computer Vision: Enhancing Search Experience with High-Dimensional Vectors
Challenges and Limitations
While computer vision has many potential applications in manufacturing, there are also some challenges and limitations to consider.
- One of the main challenges is the cost of implementing computer vision systems.
- These systems can be expensive to install and maintain, and may require specialized expertise to operate.
- Additionally, computer vision systems may not be suitable for all manufacturing processes, and may require customization to meet the specific needs of each application.
- Another challenge is the need for high-quality data.
- Computer vision algorithms rely on high-quality images to accurately detect defects and anomalies. If the images are of poor quality or contain noise, the algorithms may produce inaccurate results.
- Manufacturers must ensure that their cameras and lighting systems are properly calibrated and maintained to ensure high-quality data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, computer vision has many potential applications in the manufacturing industry, from automated visual inspection to robotic automation. By using cameras and image processing algorithms, manufacturers can improve efficiency, accuracy, and safety in their production processes. While there are some challenges and limitations to consider, the benefits of computer vision in manufacturing are significant. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of computer vision in the manufacturing industry.