Light Detection and Ranging, universally known as LiDAR, is transforming the ways of navigation. Once relegated to niche applications, today Lidar stands at the vanguard of a multitude of sectors. It’s reshaping our perception and interaction with the physical world. As 2023 unfolds, the scope and applications of Lidar technology continue to expand, making it an opportune moment to explore its multifaceted uses.
In this post, we will be exploring the depths of Lidar’s capabilities. I’ll illuminate the myriad ways Lidar is shaping our world and its potential uses for tomorrow.
Unveiling the Main Benefit of LiDAR
The main benefit of using LiDAR lies in its ability to generate accurate, high-resolution 3D representations of physical environments. This accuracy stems from its advanced technology, which emits pulses of light. Light is emitted up to a million per second and then LiDAR measures the precise time. This is the time each pulse takes to bounce back after hitting an object.
This provides highly detailed, real-time data, regardless of environmental conditions or the time of day.
Training Data vs Validation Data: What is the Difference
Navigating the Terrain: Where is LiDAR Most Useful?
LiDAR’s utility extends across a plethora of sectors, ranging from autonomous vehicles to environmental monitoring.
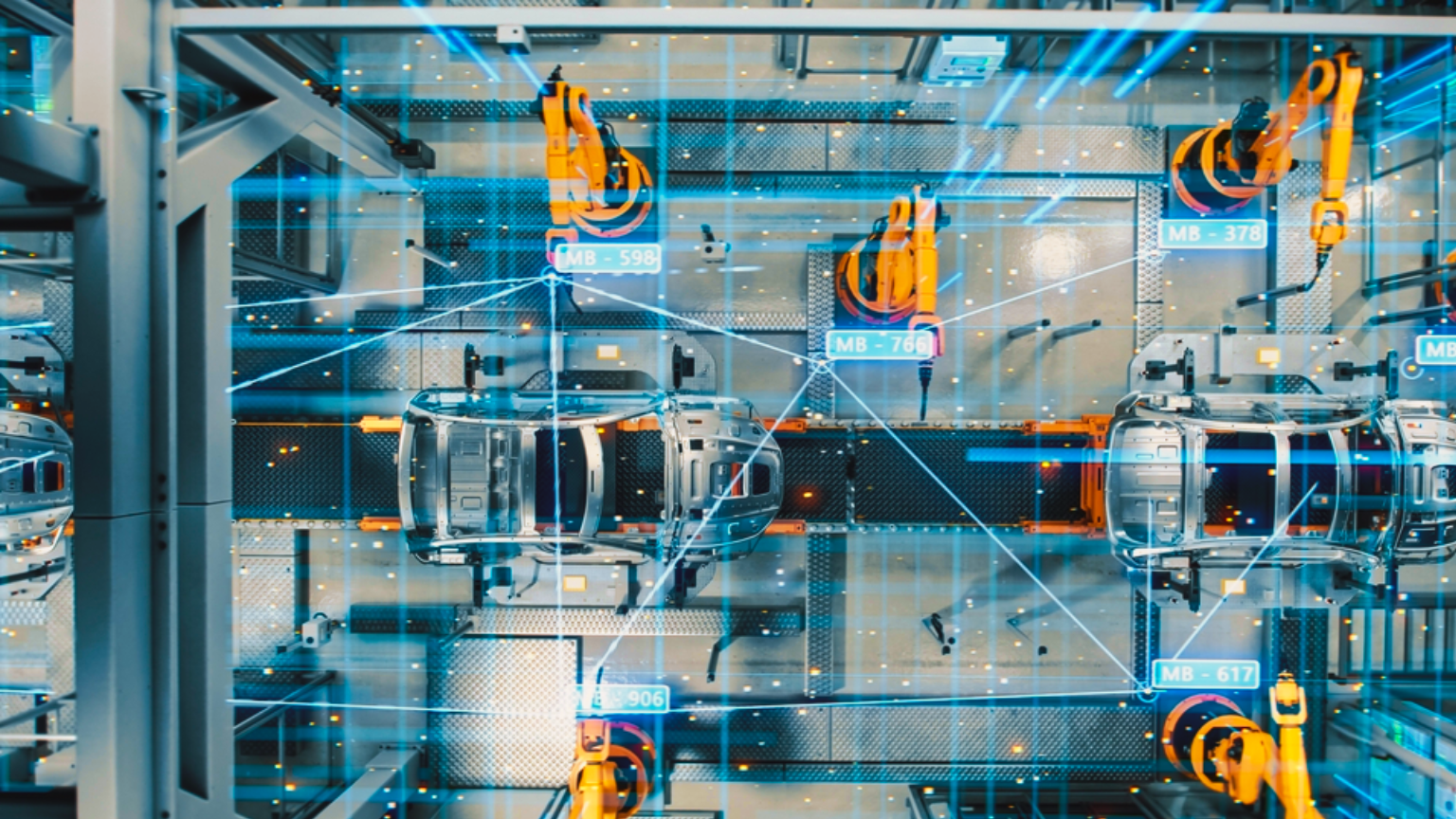
Autonomous Vehicles: Perhaps the most notable use of LiDAR is in autonomous or self-driving vehicles. These vehicles rely on LiDAR sensors to create a detailed 3D map of their surroundings. This enables the vehicles to detect obstacles, lane markings, and the road’s curvature, even under poor visibility conditions.
Surveying and Mapping: LiDAR is an invaluable tool for geospatial professionals. It aids in mapping complex terrains, modeling city structures, and exploring archaeological sites. By penetrating foliage, LiDAR can also reveal ground features hidden by dense vegetation.
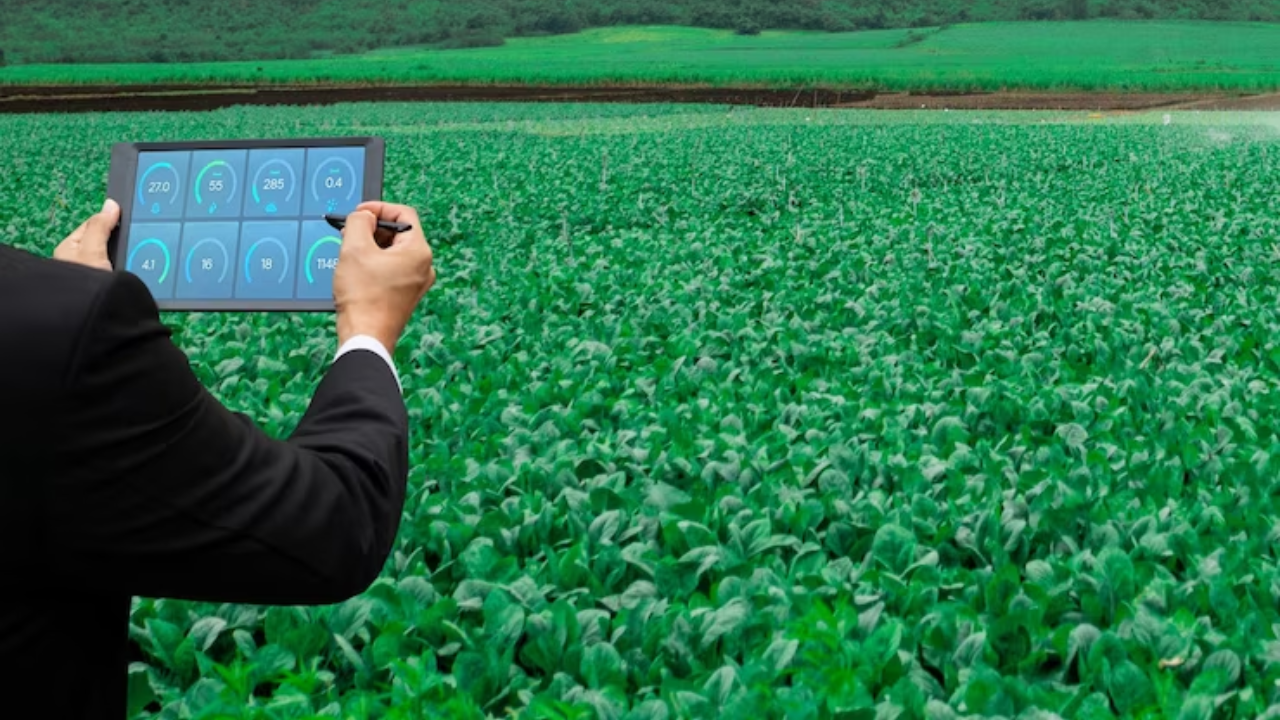
Agriculture: Farmers and agricultural scientists employ LiDAR to gather detailed topographical and vegetation data. These data inform irrigation planning, crop management, and yield estimation.
Atmospheric Research: Meteorologists and climate scientists use LiDAR to study atmospheric properties. They also use it to study the distribution of particles and gases, which is used for weather prediction and climate modeling.
Sailing Through the Waves with Bathymetric LiDAR
One remarkable application of LiDAR technology is bathymetric LiDAR. This is the technological tool used to measure seafloor and riverbed depth. Unlike typical LiDAR, which uses near-infrared light, bathymetric LiDAR uses green light wavelengths that can penetrate water. It is an efficient way of mapping large coastal and river areas. The technology aids in underwater detection, seafloor mapping, and flood risk management.
Different Shades of Perception: Types of LiDAR
There are two main types of LiDAR—airborne and terrestrial—each with specific uses.
Airborne LiDAR: Mounted on aircraft, airborne LiDAR covers large areas swiftly. This makes it ideal for topographic mapping and forestry management. It further bifurcates into topographic and bathymetric LiDAR, as discussed earlier.
Terrestrial LiDAR: Terrestrial LiDAR systems are stationed on the ground and are either static or mobile. These systems excel in detailed, high-accuracy modeling of structures, landscapes, roads, and archaeological sites.
Piercing the Darkness: Is LiDAR Used at Night?
Yes, LiDAR operates effectively both day and night. Unlike cameras that depend on light, LiDAR sensors emit their own light pulses. This makes them capable of working in complete darkness. Also, this trait makes LiDAR a cornerstone technology in applications that require round-the-clock operation. This can be helpful for autonomous vehicles and 24/7 surveillance systems.
Envisioning the Future Uses of LiDAR
As LiDAR technology continues to advance and become more accessible, its potential uses expand. In medicine, LiDAR could enable precise patient tracking and real-time monitoring for surgeries and treatments. In retail, LiDAR could streamline inventory management and facilitate autonomous checkouts. In the realm of virtual and augmented reality, high-precision LiDAR sensors could aid in creating hyper-realistic, immersive environments.
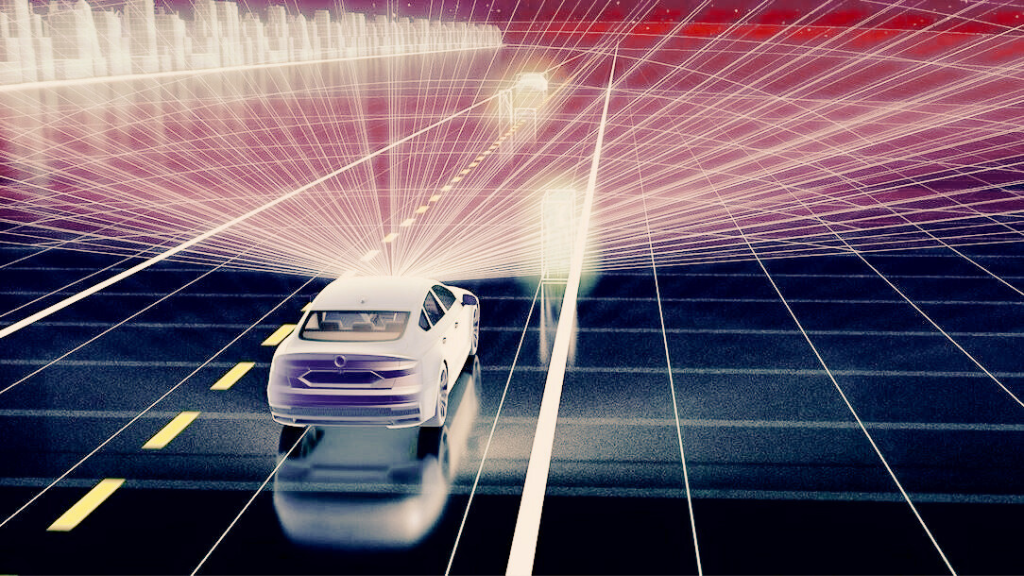

As we move further into the future, we can expect LiDAR to be a lynchpin in the development of smart cities. Its capacity for creating accurate 3D models of urban environments can contribute significantly to urban planning. The technology can also be used for infrastructure management and environmental monitoring.
Supervised Vs Unsupervised Machine Learning
Summary
LiDAR technology, with its distinctive ability to capture the world, is an indomitable force across diverse sectors. It can be used to illuminate unseen features beneath dense forest canopies and deep waters as well as for guiding the vehicles of the future. As technology continues to evolve and become more widely adopted, there is no telling where its light will shine next.
FAQs
What does LiDAR stand for and how does it work?
What is the main benefit of using LiDAR?
Where is LiDAR most commonly used?
What is bathymetric LiDAR and how is it used?
Can LiDAR be used at night?
What are the different types of LiDAR?
What are potential future uses for LiDAR?
References
- https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/lidar.html#:~:text=Lidar%20data%20supports%20activities%20such,surveying%2C%20and%20coastal%20vulnerability%20analysis.
- https://www.americangeosciences.org/critical-issues/faq/what-lidar-and-what-it-used
- https://www.neonscience.org/resources/learning-hub/tutorials/lidar-basics
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lidar