Data lake is a way to store big data that is unstructured but still valuable, such as social sentiment or advertising results. It can work with both a data warehouse and a database, but it requires careful management to avoid becoming a “data swamp.” On the other hand, a data warehouse is a more structured way to store data that has already been processed and is ready for analysis. It is typically used for business intelligence and reporting purposes.
Understanding Data Lakes
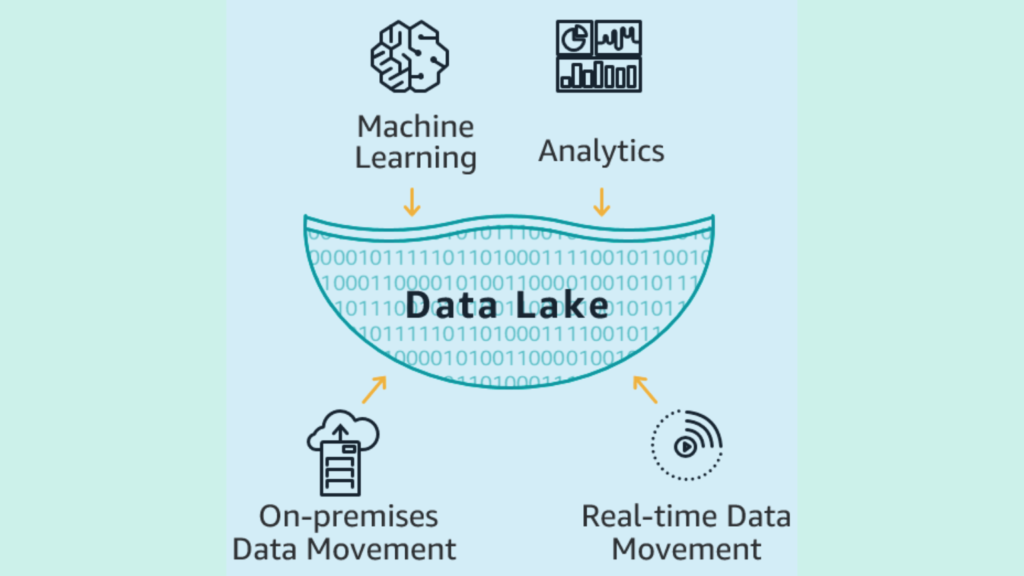
Data lake is a way to store big data that is unstructured but still valuable, such as social sentiment or advertising results. It is a repository that allows organizations to store all their structured and unstructured data at any scale. Data lakes enable organizations to store data in its raw format, without having to structure it beforehand, and then process it on an as-needed basis. However, it requires careful management to avoid becoming a “data swamp.”
Power Your Analytics with the Best Business Intelligence Dataset
What is Data Warehouses
A data warehouse is a more structured way to store data that has already been processed and is ready for analysis. It is typically used for business intelligence and reporting purposes. Data warehouses are designed to support the efficient querying and analysis of data, and they often use a schema-on-write approach, which means that data is structured and organized before it is loaded into the warehouse. This makes it easier to analyze and report on the data, but it can also make it more difficult to work with unstructured data or data that doesn’t fit neatly into predefined categories.

Key Differences Between Data Lake and Data Warehouse
1. Data Structure:
Data lakes store raw, unstructured data, while data warehouses store structured, processed data.
2. Data Processing:
Data lakes process data on an as-needed basis, while data warehouses process data before it is loaded into the warehouse.
3. Data Variety:
Data lakes can store a wide variety of data types, including unstructured data, while data warehouses are typically limited to structured data.
4. Data Storage:
Data lakes can store data at any scale, while data warehouses are typically limited in size and require careful management to avoid performance issues.
5. Data Use:
Data lakes are often used for exploratory data analysis and machine learning, while data warehouses are typically used for business intelligence and reporting.
Why a Data Lake and Not a Data Warehouse?
a data lake may be a better choice than a data warehouse in certain situations. One reason is that data lakes can store a wider variety of data types, including unstructured data, which can be difficult to work with in a data warehouse. Additionally, data lakes can store data at any scale, making them a good choice for organizations that need to store large amounts of data.
Data lakes also allow for more flexible data processing, as data can be processed on an as-needed basis, rather than being processed before it is loaded into the warehouse. That’s why it’s a cost effective solution. Finally, data lakes are often used for exploratory data analysis and machine learning, which may not be well-suited to a data warehouse environment. However, it’s important to note that data lakes require careful management to avoid becoming a “data swamp,” and they may not be the best choice for all organizations or use cases.
Data Warehouse vs Data Mart: A Detailed Comparison