Machine learning is a rapidly growing field that has transformed our approach to data analysis. This involves algorithms and statistical models that derive insights without being explicitly programmed. Broadly speaking, machine learning models fall into two categories: supervised and unsupervised learning. In this guide, let’s delve into the distinctions between these two paradigms and how they’re leveraged in data mining.
Supervised Vs Unsupervised Machine Learning
Supervised Learning
At its core, supervised learning involves the use of labeled data to train a model to make predictions or classifications. The labeled data consists of input variables (also known as features) and output variables (also known as labels or targets). The goal of supervised learning is to learn a mapping function that can predict the output variable given the input variables. Examples of supervised learning algorithms include neural networks, decision trees, and support vector machines.
Neural Networks
Type of supervised learning algorithm that is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. They consist of multiple layers of interconnected nodes (also known as neurons) that process and transmit information. Neural networks are used for a wide range of applications such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing.
Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP)
Multi-layer perceptron (MLP) is a type of neural network that consists of multiple layers of nodes. Each node in the input layer represents an input variable, and each node in the output layer represents an output variable. The nodes in the hidden layers perform computations on the input variables to generate the output variables.
Decision Trees
Decision trees are a type of supervised learning algorithm that is used for classification and regression tasks. They consist of a tree-like structure where each node represents a decision based on a feature of the input data. The leaves of the tree represent the output variables.
Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
Support vector machines (SVMs) are a type of supervised learning algorithm that is used for classification and regression tasks. They work by finding the hyperplane that maximally separates the data into different classes. SVMs are widely used in various applications such as image recognition, text classification, and bioinformatics.
Tesla Robots Are Losing Direction | Robot SLAM
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning involves the use of unlabeled data to discover patterns and relationships in the data. The goal of unsupervised learning is to learn the underlying structure of the data without any prior knowledge of the output variable. Unsupervised learning is widely used in various applications such as anomaly detection, clustering, and dimensionality reduction.
Clustering
Clustering is a type of unsupervised learning algorithm that is used to group similar data points together. The goal of clustering is to partition the data into groups (also known as clusters) based on similarities. Clustering is widely used in various applications such as customer segmentation, image segmentation, and document clustering.
K-Means
A popular clustering algorithm that is used to partition the data into K clusters. The algorithm works by randomly selecting K centroids (also known as cluster centers) and assigning each data point to the nearest centroid. The centroids are then updated based on the mean of the data points assigned to each cluster. The algorithm iteratively repeats these steps until convergence.
Self-Organizing Maps (SOMs)
Self-organizing maps (SOMs) are a type of unsupervised learning algorithm that is used for dimensionality reduction and visualization. SOMs consist of a grid of nodes that are arranged in a two-dimensional space. Each node represents a weight vector that is updated based on the input data. The nodes that are close to each other in the grid represent similar data points.
Ensembles in Machine Learning
Type of machine learning technique that combines multiple models to improve the accuracy of predictions. Ensembles are widely used in various applications such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing.
Bagging
Type of ensemble technique that involves training multiple models on different subsets of the data and combining their predictions. Bagging is widely used in various applications such as random forests and gradient boosting.
Boosting
Type of ensemble technique that involves training multiple models sequentially, where each model is trained to correct the errors of the previous model. Boosting is widely used in various applications such as AdaBoost and XGBoost.
Beyond Supervised and Unsupervised Learning
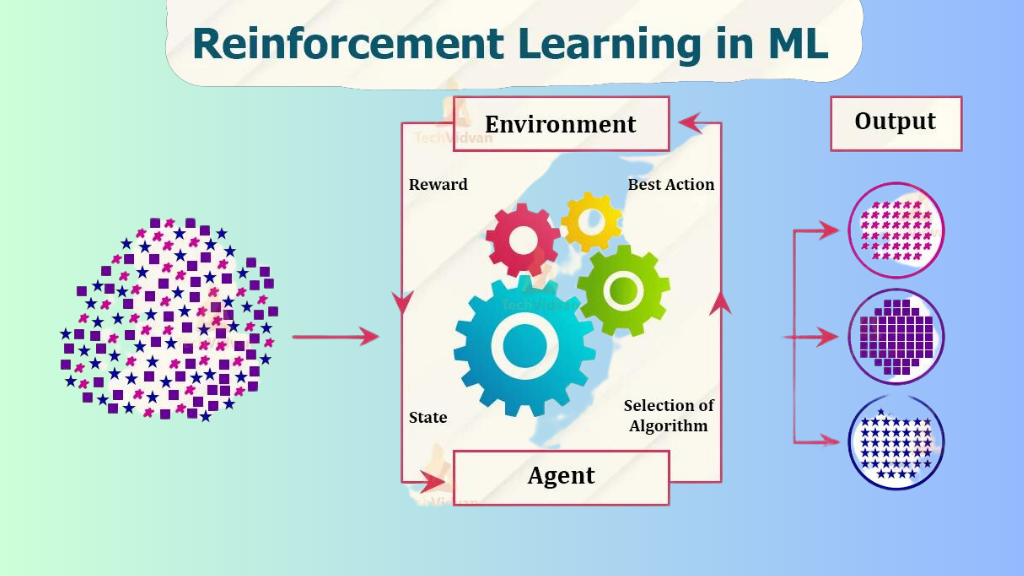
Another vital branch of machine learning deserves mention: reinforcement learning. It’s a type where an agent learns to make decisions by taking actions in an environment to maximize some reward. The agent isn’t provided with correct input/output pairs or explicitly told to find hidden structures. Instead, it learns from rewards and punishments, distinguishing it from both supervised and unsupervised learning.
Conclusion
Supervised and unsupervised learning are two fundamental approaches to machine learning that have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Supervised learning is used when the output variable is known, and the goal is to learn a mapping function that can predict the output variable given the input variables. Unsupervised learning is used when the output variable is unknown, and the goal is to learn the underlying structure of the data. By understanding the differences between these two approaches, data scientists can choose the right approach for their specific data mining tasks and make informed decisions that lead to better insights and predictions.